希望长大对我而言,是可以做更多想做的事,而不是被迫做更多不想做的事...... 首页 Elasticsearch之shard、replica、扩容、容错过程 丁D 学无止境 2019-08-26 09:42 87341已阅读 Elasticsearch primary shard replica shard 摘要本次将再次梳理一下es的shard&replica,分析横向扩容和容错过程 ###shard&replica机制再次梳理 (1)index包含多个share (2)每个shard都是一个最小的工作单元,承载部分数据,lucene实例,有完整的建立索引和处理请求的能力。 (3)增删节点的时候,share会自动平衡 (4)primary shard和replica shard,没有document肯定存在在一个primary shard和replica shard,不会同时存在多个 (5)replica是primary的副本,具有容错和备份,分担读请求的功能 (6)primary在创建索引的时候就固定了,不能修改,replica可以随时修改 (7)primary shard默认是5个,replica默认是1个,那共有10个shard,5个primary,5个replica (8)primary和replica是不能再一个node的,否则节点宕机就崩了。replica就起不到容错的作用 ###单个node,创建index ```js PUT /test_index { "settings" : { "number_of_shards" : 3, "number_of_replicas" : 1 } } ``` (1)这样创建会有3个primary和每个primary有1个replica,共有6个shards, (2)由于只有一个node,所以3个primary会被分配到同一个node,但是replica没有分配,集群状态是yellow, (3)集群可以正常提供服务,但是当node宕机,集群就无法提供服务 ###文档的元数据 节点| 说明 ------- | ------- _index| 文档存储的地方,相当数据库,只能小写,不能下划线开头,不能含有逗号等 _type |文档相同结构的对象,相当表,可以是大写或小写,不能下划线开头,不能含有逗号 _id| 与indexhe type结合,可以代表唯一,创建一个文档,你可以自定义_id,也可以让Elasticsearch帮你自动生成 ###扩容过程和容错分析 假设我们index 目前设置有 3个primary和3个replica 共6个shard 并且shard分布如下图 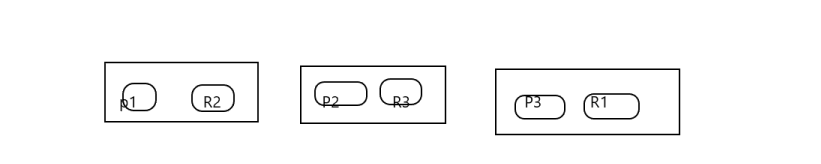 (1)每个node的shard越少,分配给当前node的shard的资源更多(IO,CPU,内存),每个shard的性能就会更高 (2)当前6个shard,所以如果有6个node,每个node就一个shard,shard就能占用node所有的资源,这时候性能最好 (3)超出扩容的极限我们可以设置 replica=2 每个primary有2个副本,就共有9个shard就可以扩容到9台服务器,吞吐量就有3倍了。 (4)3台node 6个shard的情况下,可以宕机1台机器 假设第一台服务器宕机了,其他2台还是有全部的数据,所以集群能继续提供服务。 宕机的一瞬间集群状态是red的(不是所有的primary都是active),master会将第3台node的R1升级为primary,并将p2的复制一份到第3台机器,将P1的副本放在第二台(集群成green)。 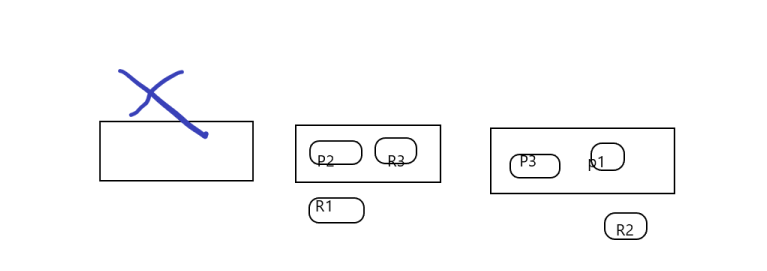 (5)3个primary,6个replica,共9个shard 3个node 分析如下图 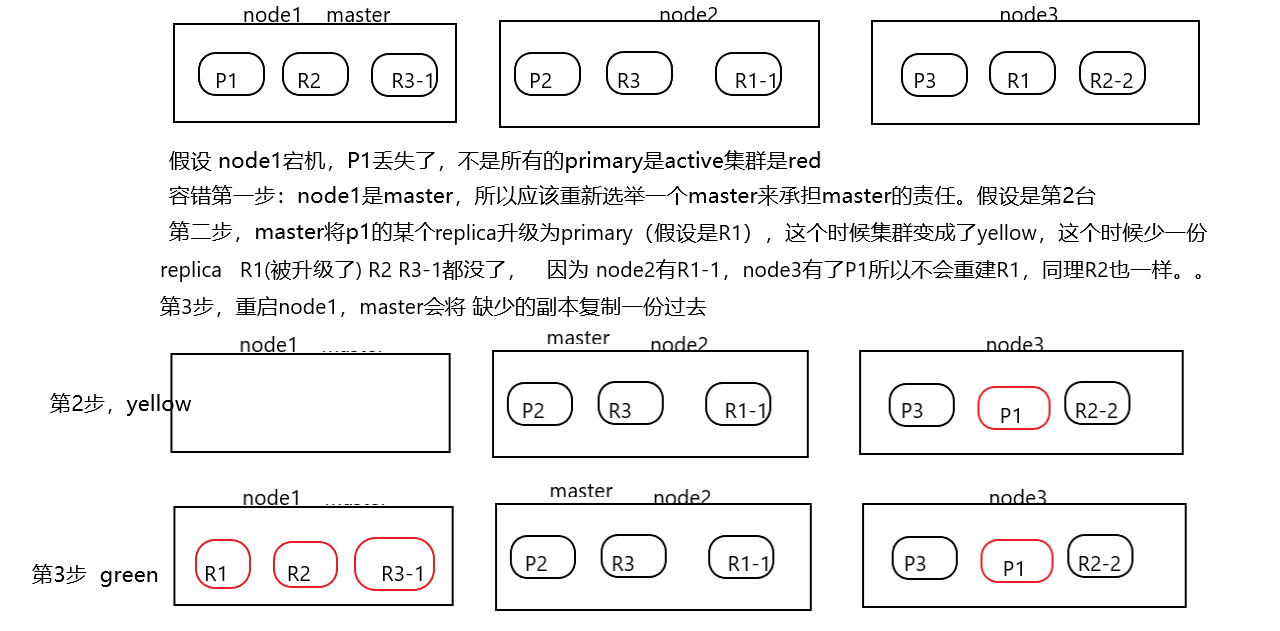 **bool 查询** should只有增加分数,没有过滤作用 bool 查询与 bool 过滤相似,用于合并多个查询子句。不同的是,bool 过滤可以直接给出是否匹配成功, 而bool 查询要计算每一个查询子句的 _score (相关性分值)。 must:: 查询指定文档一定要被包含。 must_not:: 查询指定文档一定不要被包含。 should:: 查询指定文档,有则可以为文档相关性加分。 以下查询将会找到 title 字段中包含 "how to make millions",并且 "tag" 字段没有被标为 spam。 如果有标识为 "starred" 或者发布日期为2014年之前,那么这些匹配的文档将比同类网站等级高: ```js { "bool": { "must": { "match": { "title": "how to make millions" }}, "must_not": { "match": { "tag": "spam" }}, "should": [ { "match": { "tag": "starred" }}, { "range": { "date": { "gte": "2014-01-01" }}} ] } } ``` ```js //查询 价格1000,并且name含有test关键字的 //注意跟下一段代码区分 GET /tea/product/_search { "query": { "bool": { "must": [{ "term": { "price": 1000 } }], "filter": { "bool": { "should": [{ "term": { "name": "test" } }] } } } } } 这个也可以做到 { "query": { "bool": { "must": [ { "term": { "price": 1000 } }, { "bool": { "should": [ { "term": { "name": "test" } } ] } } ] } } } 返回 1条 name有test { "took": 4, "timed_out": false, "_shards": { "total": 5, "successful": 5, "failed": 0 }, "hits": { "total": 1, "max_score": 1, "hits": [ { "_index": "tea", "_type": "product", "_id": "5", "_score": 1, "_source": { "name": "test tea", "desc": "test tea", "price": 1000, "tags": [ "test" ] } } ] } } ``` ```js 当must和should同级的时候 should 没有过滤的作用只有增加score的作用 GET /tea/product/_search { "query": { "bool": { "must": [{ "term": { "price": 1000 } }], "should": [ { "term": { "name": "test" } } ] } } } 返回有两个价格1000的,但是name 无效,,是因为这个时候should只是提高分数 { "took": 5, "timed_out": false, "_shards": { "total": 5, "successful": 5, "failed": 0 }, "hits": { "total": 2, "max_score": 1.258116, "hits": [ { "_index": "tea", "_type": "product", "_id": "5", "_score": 1.258116, "_source": { "name": "test tea", "desc": "test tea", "price": 1000, "tags": [ "test" ] } }, { "_index": "tea", "_type": "product", "_id": "1", "_score": 1, "_source": { "name": "wu long tea", "price": 1000, "desc": "this is good tea", "tags": [ "yangsheng", "meiyan" ] } } ] } } ``` **term 精确查询** 比如Id,数值类型的查询。 可以用它处理数字(numbers)、布尔值(Booleans)、日期(dates)以及文本(text)。 ```js 假设我要查询价格1000 name含有test tea 这个短语的 GET /tea/product/_search { "query": { "bool": { "must": [{ "term": { "price": 1000 } }], "filter": { "bool": { "should": [{ "term": { "name": "test tea" } }] } } } } } 返回 null 没有查询到 //主要是因为term 不会讲查询关键字进行分词。,,,但是es库中的词语已经被分词了 //所以查询不到 { "took": 2, "timed_out": false, "_shards": { "total": 5, "successful": 5, "failed": 0 }, "hits": { "total": 0, "max_score": null, "hits": [] } } ``` **查看分词情况** ```js 查看分词情况 GET /tea/_analyze { "field": "name", //字段 "text": "test tea"//文本 } 结果 { "tokens": [ { "token": "test", "start_offset": 0, "end_offset": 4, "type": "<ALPHANUM>", "position": 0 }, { "token": "tea", "start_offset": 5, "end_offset": 8, "type": "<ALPHANUM>", "position": 1 } ] } ``` 提示: 如果bool 查询下没有must子句,那至少应该有一个should子句。但是 如果有must子句,那么没有should子句也可以进行查询。 **id的指定或自动生成** 1.一般来说如果从第三方库导入es中的,一般通过指定id的形式,使用**put** ```js put /index/type/id PUT /test_index/test_type/2 { "test_content": "my test" } ``` 2.一般来说,如果是新系统,并确定主要数据放在es,可以使用es自动生成id的形式 使用**post** 自动生成的id,**长度为20个字符**,URL安全,base64编码,GUID,分布式系统并行生成时不可能会发生冲突 ```js post /index/type POST /test_index/test_type { "test_content": "my test" } { "_index": "test_index", "_type": "test_type", "_id": "AVp4RN0bhjxldOOnBxaE", "_version": 1, "result": "created", "_shards": { "total": 2, "successful": 1, "failed": 0 }, "created": true } ``` **返回特定的字段** ```js GET /test_index/test_type/1?_source=test_field1 ``` **文档的全量更新** ```js 文档的全量更新跟创建的时候put一样 put /index/type/1 { ... } 会替换旧的。。 将旧的文档标记为deleted,当我们创建越来越多的document的时候,es会在适当的时机在后台自动删除标记为deleted的document ``` **强制创建** ```js //因为put创建和全量更新一样。 //但是有时候我们需要的是创建,而不是更新。所以可以使用_create来强制创建,如果id已经存在那么会报错 PUT /index/type/id/_create { ... } ``` **document的删除** ```js (1)DELETE /index/type/id (2)不会理解物理删除,只会将其标记为deleted,当数据越来越多的时候,在后台自动删除 ``` **并发冲突--version** 假设在电商场景中,我们经常会遇到多个web进程同时对一个商品进行操作。 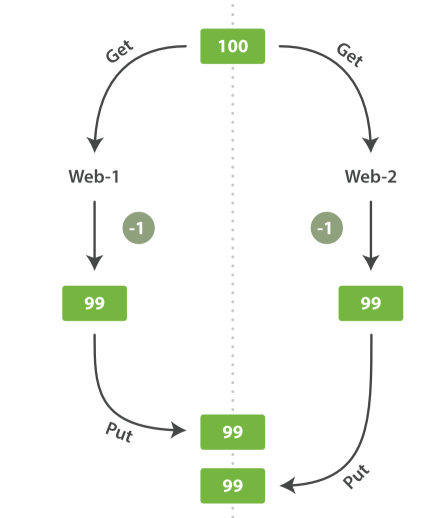 如上图 我们就会发现出现了修改丢失的情况 在关系型数据库中,通常使用的是**悲观锁**,而在es中使用的**乐观锁** 在es中我们使用的是version这个field来控制 ```js 如下:我们修改只有在version=9的时候才会生效。只有相等的时候, PUT /tea/product/1?version=9 { "price":999, "desc": "this is good tea", "tags": [ "yangsheng", "meiyan" ] } ``` **并发冲突----外部版本控制系统** 我们也可能遇到这种情况 数据库的数据要同步到es中。。当我们多个进程在同步的时候可能出现old版本覆盖new的版本。 如果主数据库有版本字段——或一些类似于timestamp等可以用于版本控制的字段——是你就可以在Elasticsearch的查询字符串后面添加**version_type=external**来使用这些版本号。版本号必须是**整数**,大于零小于9.2e+18——Java中的正的**long**。 外部版本号与之前说的内部版本号在处理的时候有些不同。**它不再检查_version是否与请求中指定的一致,而是检查是否小于指定的版本**。如果请求成功,外部版本号就会被存储到_version中。 ```js version=11要大于原本es中的version (要大于,等于小于都不行(409错误)) PUT /tea/product/1?version=11&version_type=external { "price":999, "desc": "this is good tea", "tags": [ "yangsheng", "meiyan" ] } ``` **mget批量查询** mget可以批量查询,减少网络的开销 ```js //查询不同的index,不同的type //docs放在数组中,_source可以定制 POST /_mget { "docs" : [ { "_index" : "website", "_type" : "blog", "_id" : 2 }, { "_index" : "website", "_type" : "pageviews", "_id" : 1, "_source": "views" } ] } 返回 通过found来判断是不是查询到了 ,返回放在docs数组 { "docs" : [ { "_index" : "website", "_id" : "2", "_type" : "blog", "found" : true, "_source" : { "text" : "This is a piece of cake...", "title" : "My first external blog entry" }, "_version" : 10 }, { "_index" : "website", "_id" : "1", "_type" : "pageviews", "found" : true, "_version" : 2, "_source" : { "views" : 2 } } ] } ``` **批量更新,创建,删除** ```js 参考:https://es.xiaoleilu.com/030_Data/55_Bulk.html ``` head判断存不存在 只有响应头没有响应体 批量 问题1 master选举规则 问题2 多个副本选择那个的规则 很赞哦! (0) 上一篇:Elasticsearch初识、document CRUD、聚合分析 下一篇:分布式系统的接口幂等性设计 目录 点击排行 Elasticsearch6.3.2之x-pack redis哨兵 2019-07-09 22:05 Redis+Twemproxy+HAProxy+Keepalived 2019-07-12 17:20 GC优化策略和相关实践案例 2019-10-10 10:54 JVM垃圾回收器 2019-10-10 10:23 标签云 Java Spring MVC Mybatis Ansible Elasticsearch Redis Hive Docker Kubernetes RocketMQ Jenkins Nginx 友情链接 郑晓博客 佛布朗斯基 凉风有信 南实博客 Rui | 丁D Java研发工程师 生活可以用「没办法」三个字概括。但别人的没办法是「腿长,没办法」、「长得好看,没办法」、「有才华,没办法」。而你的没办法,是真的没办法。 请作者喝咖啡